Introduction
- Configure Anyconnect VPN Client On FTD: DHCP Server .. - Cisco
- See Full List On Techsoup.org
- Cisco Anyconnect Vpn Settings File
- See Full List On Cisco.com
Download the VPN installer from MIT's download page, Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client for Windows. Aug 19, 2019 How To Set Up Cisco AnyConnect VPN. When it comes to setting up Cisco AnyConnect VPN, the approach to take will depend on the device you're installing it on. However, once installed the setup is very straightforward. Getting Cisco AnyConnect is as simple as navigating over to the Cisco website and downloading it.
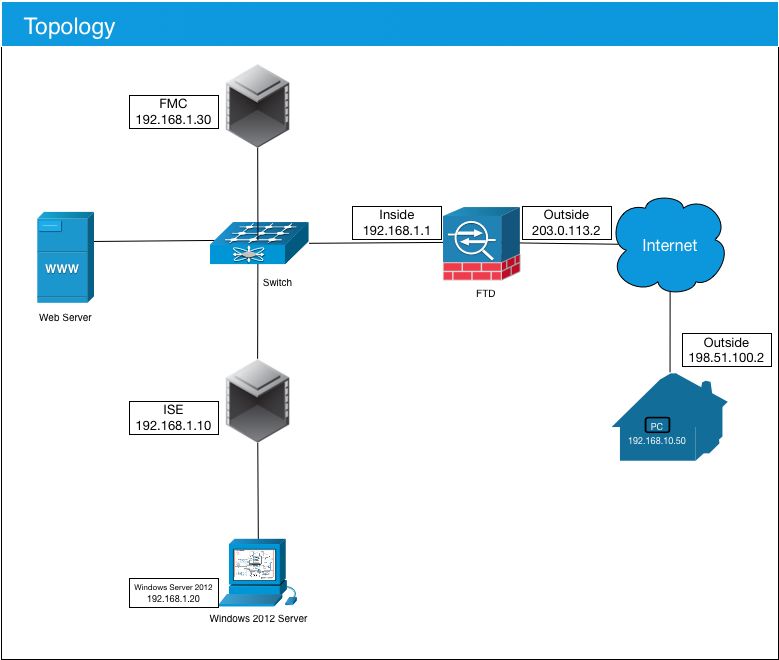
This document provides a configuration example for Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) version 6.2.2 and later, that allows remote access VPN to use Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2). As a client, Cisco AnyConnect will be used, which is supported on multiple platforms.
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
Configure Anyconnect VPN Client On FTD: DHCP Server .. - Cisco
- Basic VPN, TLS and IKEv2 knowledge
- Basic Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) and RADIUS knowledge
- Experience with Firepower Management Center
Components used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- Cisco FTD 6.2.2
- AnyConnect 4.5
Configuration
1. Preresiquites
In order to go through Remote Access wizard in Firepower Management Center, first you will need to follow these steps:
- create a certificate used for server authentication,
- configure RADIUS or LDAP server for user authentication,
- create pool of addresses for VPN users,
- upload AnyConnect images for different platforms.
a) importing SSL certificate
Certificates are essential when you configure AnyConnect. Only RSA based certificates are supported in SSL and IPSec. Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm certificates (ECDSA) are supported in IPSec, but it's not possible to deploy new AnyConnect package or XML profile when ECDSA based certificate is used. It means that you can use it for IPSec, but you will have to predeploy AnyConnect package and XML profile to every user and any change in XML profile will have to be manually reflected on each client (bug: CSCtx42595). Additionally the certificate should have Subject Alternative Name extension with DNS name and/or IP address to avoid errors in web browsers.
There are several methods to obtain a certificate on FTD appliance, but the safe and easy one is to create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), sign it and then import certificate issued for public key, which was in CSR. Here is how to do that:
- Go to Objects > Object Management > PKI > Cert Enrollment, click on Add Cert Enrollment:
- Select Enrollment Type and paste Certificate Authority (CA) certificate,
- Then go to second tab and select Custom FQDN and fill all necessary fields, eg.:
- On the third tab, select key type, choose name and size. For RSA, 2048 bytes is minimum.
- Click save and go to Devices > Certificates > Add > New Certificate. Then select Device, and under Cert Enrollment select the trustpoint which you just created, click Add:
See Full List On Techsoup.org
- Later, next to the trustpoint name, click on icon, then Yes and after that copy CSR to CA and sign it. Certificate should have attributes as normal HTTPS server.
- After receiving certificate from CA in base64 format, select it from the disk and click Import. When this succeeds, you should see:
b) configure RADIUS server
On FTD platftorm, local user database cannot be used, so you need RADIUS or LDAP server for user authentication. To configure RADIUS:
- Go to Objects > Object Management > RADIUS Server Group > Add RADIUS Server Group.
- Fill the name and add IP address along with shared secret, click Save:
- After that you should see server on the list:
c) creating pool of addresses for VPN users
- Go to Objects > Object Management > Address Pools > Add IPv4 Pools:
- Put the name and range, mask is not needed:
d) creating XML profile
- Download Profile Editor from Cisco site and open it.
- Go to Server List > Add..
- Put Display Name and FQDN. You should see entries in Server List:
- Click OK and File > Save as..
e) uploading AnyConnect images
- Download pkg images from Cisco site.
- Go to Objects > Object Management > VPN > AnyConnect File > Add AnyConnect File.
- Type the name and select PKG file from disk, click Save:
- Add more packages depending on your requirements.
2. Remote access wizard
- Go to Devices > VPN > Remote Access > Add a new configuration.
- Name the profile according to your needs, select FTD device:
- In step Connection Profile, type Connection Profile Name, select Authentication Server and Address Pools which you have created earlier:
- Click on Edit Group Policy and on the tab AnyConnect, select Client Profile, then click Save:
- On the next page, select AnyConnect images and click Next:
- On the next screen, select Network Interface and DeviceCertificates:
- When everything is configured correctly, you can click Finish and then Deploy:
- This will copy whole configuration along with certificates and AnyConnect packages to FTD appliance.
Connection
To connect to FTD you need to open a browser, type DNS name or IP address pointing to the outside interface, in this example https://vpn.cisco.com. You will then have to login using credentials stored in RADIUS server and follow instructions on the screen. Once AnyConnect installs, you then need to put the same address in AnyConnect window and click Connect.
Limitations
Currently unsupported on FTD, but available on ASA:
- Double AAA Authentication
- Dynamic Access Policy
- Host Scan
- ISE posture
- RADIUS CoA
- VPN load-balancer
- Local authentication (Enhancement: CSCvf92680)
- LDAP attribute map
- AnyConnect customization
- AnyConnect scripts
- AnyConnect localization
- Per-app VPN
- SCEP proxy
- WSA integration
- SAML SSO
- Simultaneous IKEv2 dynamic crypto map for RA and L2L VPN
- AnyConnect modules (NAM, Hostscan, AMP Enabler etc.) – DART is installed by default
- TACACS, Kerberos (KCD Authentication and RSA SDI)
- Browser Proxy
Security considerations
You need to remember that by default, sysopt connection permit-vpn option is disabled. This means, that you need to allow traffic coming from pool of addresses on outside interface via Access Control Policy. Although the pre-filter or access-control rule is added intending to allow VPN traffic only, if clear-text traffic happens to match the rule criteria, it is erroneously permitted. AnyConnect VPN Client FAQ.
There are two approaches to this problem. First, TAC recommended option, is to enable Anti-Spoofing (on ASA known as Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding - uRPF) for outside interface, and the second is to enable sysopt connection permit-vpn to bypass Snort inspection completely. First option allows to normally inspect traffic going to and from VPN users.
a) Enabling uRPF
- create a null route for network used for remote access users, defined in section c. Just go to Devices > Device Management > Edit > Routing > Static Route > Add route:
- secondly, you need to enable uRPF on the interface which is terminating VPN connections. You can find it in Devices > Device Management > Edit > Interfaces > Edit > Advanced > Security Configuration > Enable Anti Spoofing:
When user is connected, 32-bit route is installed for that user in routing table. Clear text traffic sourced from other, unused IP addresses from the pool is dropped by uRFP. Anti-Spoofing has been described on this page:
b) Enabling sysopt connection permit-vpn option
- If you have version 6.2.3 or above, there is an option to do it during wizard or under Devices > VPN > Remote Access > VPN Profile > Access Interfaces:
Cisco Anyconnect Vpn Settings File

- Go to Objects > Object Management > RADIUS Server Group > Add RADIUS Server Group.
- Fill the name and add IP address along with shared secret, click Save:
- After that you should see server on the list:
c) creating pool of addresses for VPN users
- Go to Objects > Object Management > Address Pools > Add IPv4 Pools:
- Put the name and range, mask is not needed:
d) creating XML profile
- Download Profile Editor from Cisco site and open it.
- Go to Server List > Add..
- Put Display Name and FQDN. You should see entries in Server List:
- Click OK and File > Save as..
e) uploading AnyConnect images
- Download pkg images from Cisco site.
- Go to Objects > Object Management > VPN > AnyConnect File > Add AnyConnect File.
- Type the name and select PKG file from disk, click Save:
- Add more packages depending on your requirements.
2. Remote access wizard
- Go to Devices > VPN > Remote Access > Add a new configuration.
- Name the profile according to your needs, select FTD device:
- In step Connection Profile, type Connection Profile Name, select Authentication Server and Address Pools which you have created earlier:
- Click on Edit Group Policy and on the tab AnyConnect, select Client Profile, then click Save:
- On the next page, select AnyConnect images and click Next:
- On the next screen, select Network Interface and DeviceCertificates:
- When everything is configured correctly, you can click Finish and then Deploy:
- This will copy whole configuration along with certificates and AnyConnect packages to FTD appliance.
Connection
To connect to FTD you need to open a browser, type DNS name or IP address pointing to the outside interface, in this example https://vpn.cisco.com. You will then have to login using credentials stored in RADIUS server and follow instructions on the screen. Once AnyConnect installs, you then need to put the same address in AnyConnect window and click Connect.
Limitations
Currently unsupported on FTD, but available on ASA:
- Double AAA Authentication
- Dynamic Access Policy
- Host Scan
- ISE posture
- RADIUS CoA
- VPN load-balancer
- Local authentication (Enhancement: CSCvf92680)
- LDAP attribute map
- AnyConnect customization
- AnyConnect scripts
- AnyConnect localization
- Per-app VPN
- SCEP proxy
- WSA integration
- SAML SSO
- Simultaneous IKEv2 dynamic crypto map for RA and L2L VPN
- AnyConnect modules (NAM, Hostscan, AMP Enabler etc.) – DART is installed by default
- TACACS, Kerberos (KCD Authentication and RSA SDI)
- Browser Proxy
Security considerations
You need to remember that by default, sysopt connection permit-vpn option is disabled. This means, that you need to allow traffic coming from pool of addresses on outside interface via Access Control Policy. Although the pre-filter or access-control rule is added intending to allow VPN traffic only, if clear-text traffic happens to match the rule criteria, it is erroneously permitted. AnyConnect VPN Client FAQ.
There are two approaches to this problem. First, TAC recommended option, is to enable Anti-Spoofing (on ASA known as Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding - uRPF) for outside interface, and the second is to enable sysopt connection permit-vpn to bypass Snort inspection completely. First option allows to normally inspect traffic going to and from VPN users.
a) Enabling uRPF
- create a null route for network used for remote access users, defined in section c. Just go to Devices > Device Management > Edit > Routing > Static Route > Add route:
- secondly, you need to enable uRPF on the interface which is terminating VPN connections. You can find it in Devices > Device Management > Edit > Interfaces > Edit > Advanced > Security Configuration > Enable Anti Spoofing:
When user is connected, 32-bit route is installed for that user in routing table. Clear text traffic sourced from other, unused IP addresses from the pool is dropped by uRFP. Anti-Spoofing has been described on this page:
b) Enabling sysopt connection permit-vpn option
- If you have version 6.2.3 or above, there is an option to do it during wizard or under Devices > VPN > Remote Access > VPN Profile > Access Interfaces:
Cisco Anyconnect Vpn Settings File
See Full List On Cisco.com
- For versions prior to 6.2.3, go to Objects > Object Management > FlexConfig > Text Object > Add Text Object.
- Create a text object variable, for example: vpnSysVar a single entry with value 'sysopt'
- Go to Objects > Object Management > FlexConfig > FlexConfig Object > Add FlexConfig Object.
- Create FlexConfig object with CLI 'connection permit-vpn':
- Insert the text object variable in flexconfig object at the start of CLI as '$vpnSysVar connection permit-vpn', click Save:
- Apply the FlexConfig object as Append and select deployment to Everytime:
- Go to Devices > FlexConfig and edit existing policy or create a new one with New Policy button.
- Add just created FlexConfig, click Save.
- Deploy the configuration to provision 'sysopt connection permit-vpn' command on the device.
This however, will remove the possibility to use Access Control Policy to inspect traffic coming from the users. You can still use VPN filter or downloadable ACL to filter user traffic.
If you see problems with Snort dropping packets from VPN users, contact TAC referencing CSCvg91399.

